基本了解
1.1,初识hello world
- script脚本形式引入vue脚本
- 存在开发版本和生产版本
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/vue/3.0.2/vue.global.prod.js"></script>- 对DOM里的指定标签指定渲染
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
content: 1,
};
},
mounted() {
setInterval(() => {
this.content += 1;
//写法二:this.$data.content += 1;
}, 1000);
},
template: "<div>{{content}}</div>",
}).mount("#root");- mount指定行为绑定那个DOM
- data函数表示数据
- mounted函数:类似生命周期函数
componentDidMount,在标签渲染后自动执行 - template: (模板)渲染到DOM内的内容
1.2,vue中如何绑定事件和面向数据编程
//实现点击事件翻转字符串
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
content: "hello world",
};
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.content = this.content.split("").reverse().join("");
},
},
template: `
<div>
{{content}}
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">reverse</button>
</div>
`,
}).mount("#root");- 函数段写在methods对象中
- 事件代理需要使用vue中
v-on:click="function"绑定事件
//实现标签显示和隐藏
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
show: true,
};
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.show = !this.show;
},
},
template: `
<div>
<span v-if="show">hello world</span>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">show/hide</button>
</div>
`,
}).mount("#root");- 标签显示与隐藏
v-if="boolean",布尔值决定标签显示
1.3,todolist了解循环和双向绑定
Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
list: [],
inputValue: "",
};
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = "";
},
},
template: `
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">submit</button>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item, index) of list">{{item}}</li>
</ul>
</div>
`,
}).mount("#root");- 双向绑定
v-model="var"input框中默认是变量值和输入框内容 - 循环
v-for="(item,index) of list"一般用在li标签中item就是对应标签应该获得的值
1.4,组件化概念/属性绑定变量
- 给主组件初始化一个变量
const app = Vue.createApp({});- 主组件渲染
app.mount("#root");- 绑定子组件
app.commponent('name', {});- 组件之间传值,参考react可知道应该是属性传值,那么怎么绑定数据给标签的一个属性
v-bind:shuxing="var"
<todoItem v-for="item of list" v-bind:content="item"/>- 同时子组件可以在props属性中获得父组件传来的属性
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
list: [],
inputValue: "",
};
},
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
this.list.push(this.inputValue);
this.inputValue = "";
},
},
template: `
<div>
<input v-model="inputValue"/>
<button v-on:click="handleBtnClick">submit</button>
<ul>
<todoItem v-for="item of list" v-bind:content="item"/>
</ul>
</div>
`,
});
app.component("todoItem", {
props: ["content"],
template: `
<li>{{content}}</li>
`,
});
app.mount("#root");基础知识
2.1组件的基本概念
- 根组件的实例是什么?
const app = Vue.createApp({});
const vm = app.mount("#root"); //其中vm就是根组件的实例- 怎么在外部访问组件的数据
//我们可以使用vm调用根组件中的数据
vm.$data.inputValue = "hhh"; //数据就会变化- 设计模式MVVM
- M: model 数据
- V:view 视图
- VM: 视图数据连接层—也就是组件
2.2生命周期函数
特定时刻,自动执行的函数
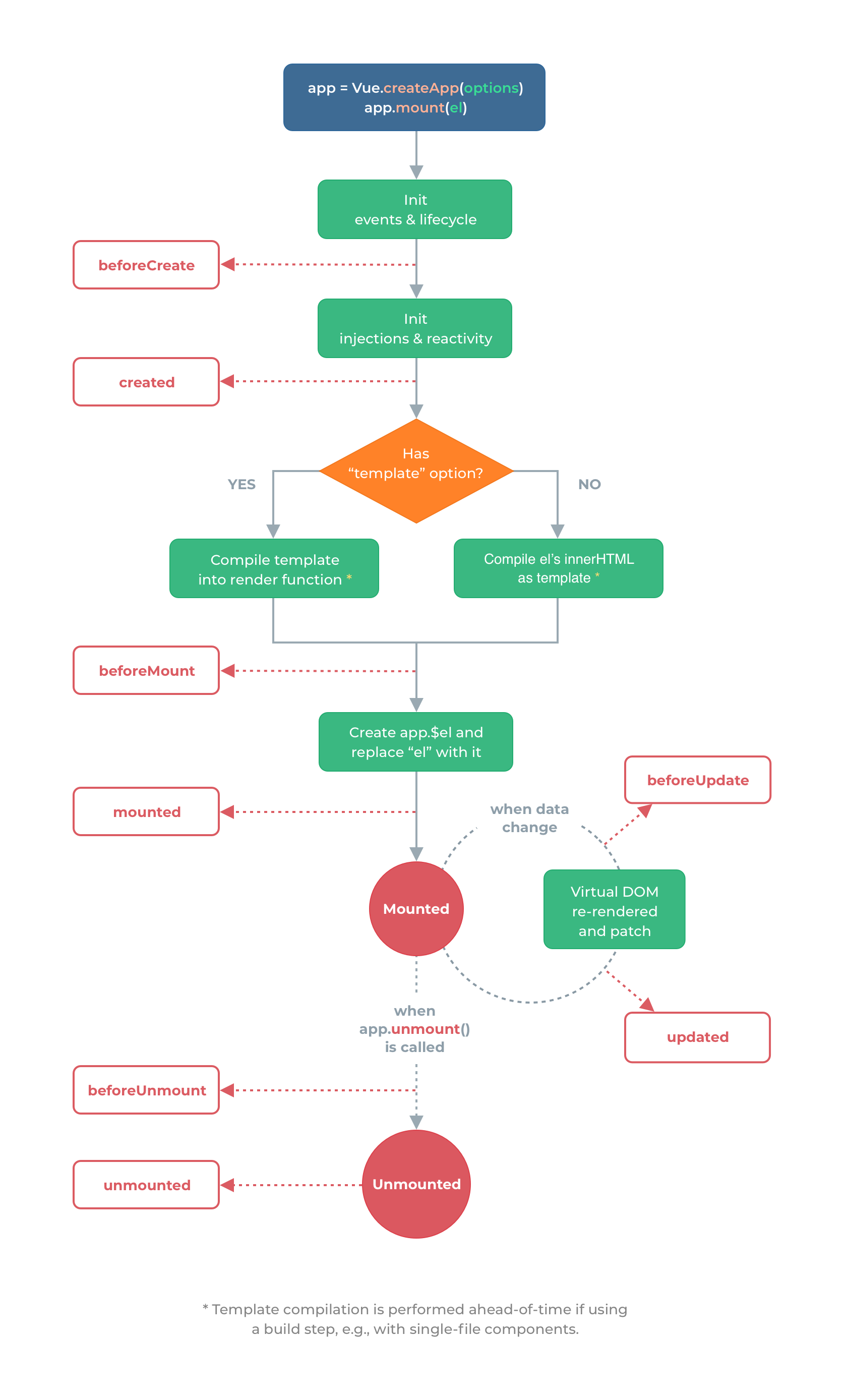
注意,中间的判断当没有template时,把挂载DOM元素的内容当做渲染的内容
四组八个:beforeCreate/created beforeMount/mounted beforeUpdate/updated beforeUnmount/unmounted
2.3常用模板语法
- 插值表达式
{{表达式}} //表达式的值- v-html
//指定内容以html文本形式解析出来
template: `<div v-html="message"></div>`- v-bind:/:
//双向绑定标签的一个指定属性和一个变量 简写 :
template: `<div v-bind:title="message">hello world</div>`
//在input框的是否可以输入上使用
template: `<input v-bind:disabled="disable">hello world</input>`- v-once
//标签内容只初次渲染
template: `<div v-once>{{message}}</div>`- v-if
//控制标签是否展示 boolean值 直接销毁DOM
template: `<div v-if="show">hello world</div>`- v-on:/@
//事件绑定 v-on:或者简写@
template: `<div @click="handleClick">hello world</div>`- 动态属性/动态事件
//根据定义的变量值来确定属性名和事件类型
template: `
<div
@[event]="handleEvent"
:[name]="message"
>
{{message}}
</div>
`- 表单阻止默认行为
//方法一:使用e.preventDefault()
methods: {
handleClick(e) {
e.preventDefault();
}
},
template: `
<form action="https://minyue-hcm.github.io" @click="handleClick">
<button type="submit">
submit
</button>
</form>
`
//方法二:使用修饰符.prevent
methods: {
handleClick(e) {
//do something else
}
},
template: `
<form
action="https://minyue-hcm.github.io"
@click.prevent="handleClick"
>
<button type="submit">
submit
</button>
</form>
`2.4Vue属性:数据,方法,计算属性,侦听器
- 数据
data() {
return {
message: 'minyue',
count: 2,
price: 5,
newTotal: 10,
}
},- 方法
//方法既可以在绑定事件中调用,也可以在插值表达式中使用(加括号)
//函数中this绑定问题 --不要使用箭头函数(指向外部window)
methods: {
formatString(string) {
return string.toUpperCase();
},
},
template: "<div>{{formatString(message)}}</div>"- 计算属性
// 只有当依赖变化 即发生变化
// 对比methods方法(只要页面重新渲染就会执行)
computed: {
total() {
return this.count*this.price;
},
},
template: '<div>{{total}}</div>'- 侦听器
//侦听数据变化,执行异步操作 也就是计算属性的底层实现
watch: {
//price发生变化时函数执行
price(current, prev) {
this.newTotal = current * this.price;
}
}2.5Vue样式绑定语法
- 类样式绑定
data() {
return {
classString: "red",
classObject: {red: true, yellow: true}
classArray: ["red", { yellow: true }],
styleString: "color: pink; background: yellow;"
styleObject: {
color: "pink",
background: "yellow",
},
};
},
//(1)html写法
template: `
<div :class="red">minyue</div>
`,
//(2)数据字符串写法
template: `
<div :class="classString">minyue</div>
`,
//(3)class对象形式
template: `
<div :class="classObject">minyue</div>
`,
//(4)class数组形式
template: `
<div :class="classArray">minyue</div>
`,- 行内样式绑定
//(1)html写法
template: `
<div style="color: pink; background: yellow;">minyue</div>
`,
//(2)数据字符串写法
template: `
<div :style="styleString">minyue</div>
`,
//(3)style对象形式 推荐!!! 注意值是字符串类型
template: `
<div :style="styleObject">minyue</div>
`,3.父子组件传递样式
//(1)子组件最外层单一节点 正常绑定
template: `
<div :style="styleObject">minyue</div>
<son class="yellow"/>
`,
//(2)子组件最外层多个节点 上面方法失效
app.component("son", {
template: `
<div :class="$attrs.class">son</div>
<div :class="$attrs.class">son</div>
`,
});2.6条件渲染
- 比较
v-ifv-show
(1)v-if 展示和隐藏会频繁生成或销毁DOM
(2)v-show 使用style="display: none"来实现不会销毁DOM- 条件渲染
data() {
return {
conditionOne: false,
conditionTwo: true,
};
},
template: `
<div v-if="show">if</div>
<div v-else-if="conditionTwo">else-if</div>
<div v-else>else</div>
`- 当conditionOne/Two同是true时,就执行if
2.7列表循环
- 对于数组而言
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
//一些数组变更函数 push/pop/unshift/shift/splice/sort/reverse
this.listArray.push("minyue");
//直接替换数组
this.listArray = ["minyue"].concat(["hello"]);
this.listArray = ["minyue","hcm"].filter(item => item === 'hcm');
//直接更新内容 --新版!!!
this.listArray[0] = 'lalala';
}
},
template: `
<div v-for="(item, index) in listArray">
{{item}}--{{index}}
</div>
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
`- 对于对象而言
methods: {
handleBtnClick() {
//直接更新内容 --新版!!!
this.listObject.age = 20;
}
},
template: `
<div v-for="(value, key, index) in listObject">
{{value}}--{{key}}--{{index}}
</div>
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
`- diff算法 给列表项添加一个惟一的key
<div v-for="(item, index) in listArray" :key="item">- 特殊用法,循环一个数字
<div v-for="item in 10">
{{index}}
</div>- 循环和判断同时存在时,循环优先级高,不能放在一起
// template类似于react中的Fragment
template: `
<template
v-for="(value, key, index) in listObject"
:key="index"
>
<div v-if="key !== age">
{{value}}--{{key}}--{{index}}
</div>
</template>
<button @click="handleBtnClick">change</button>
`2.8事件绑定
- 可表达式,可函数
template: `
<button @click="num += 1"> //可以直接写简单表达式
button
</button>
`- 函数传参
template: `
<button @click="handleBtnClick(2, $event)"> //参数 和 原生事件
button
</button>
`- 多函数绑定
//函数需要加括号,逗号隔开
template: `
<button @click="handleBtnClick(), handleClick()>
button
</button>
`- 事件修饰符
//(1)阻止事件冒泡 .stop
template: `
<div @click="handleDivClick">
<button @click.stop="handleBtnClick>button</button>
</div>
`
//(2).self 自身触发,内置冒泡的不算
template: `
<div @click.self="handleDivClick">
<button @click="handleBtnClick>button</button>
</div>
`
//(3)冒泡换成捕获 capture
template: `
<div @click.capture="handleDivClick">
<button @click="handleBtnClick>button</button>
</div>
`
//(4)阻止默认行为 .prevent
//(5)只发生一次 .once
template: `
<button @click.once="handleBtnClick>button</button>
`
// (6)scroll事件提升性能 .passive
template: `
<div @scroll.passive="handleScroll>button</div>
`- 按键修饰符 多个按键直接连写就可以
.ctrl.shift
// enter,tab,delete,esc,up,right,down,left 只有按下对应按键才会执行
// 不加修饰符就是任意按键就会触发
template: `
<input @keydown.delete="handleKeydown" />
`- 鼠标修饰符
//默认left,可以改为 .right .middle
template: `
<button @click.middle="handleBtnClick">button</button>
`,- 精确修饰符
// 当且仅当按住一个ctrl时触发 不多不少 但有点小问题
template: `
<div @click.ctrl.exact="click">sss</div>
`,2.9双向绑定
- input框的双向绑定
//不用再写value属性了
data() {
return {
message: "minyue",
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<input v-model="message" />
`,- 多行文本textarea
//类似input框
data() {
return {
message: "minyue",
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<textarea v-model="message" />
`,- 复选框 checkbox
//(1)单一选项时 数据为boolean
//(2)多选时 数据为数组 定义value属性为存放数组的内容
data() {
return {
message: [],
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
111<input v-model="message" type="checkbox" value="111"/>
222<input v-model="message" type="checkbox" value="222"/>
333<input v-model="message" type="checkbox" value="333"/>
`,
//(3)自定义选中后的展示内容
data() {
return {
message: true,
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<input v-model="message" type="checkbox" true-value="ok" false-value="no"/>
`,- 单选 radio
//数据为字符串
data() {
return {
message: "",
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
111<input v-model="message" type="radio" value="111"/>
222<input v-model="message" type="radio" value="222"/>
333<input v-model="message" type="radio" value="333"/>
`,- 下拉选项框 select
//单选 数据为字符串 value 和 message匹配
data() {
return {
message: "",
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<select v-model="message">
<option value="" disabled>请输入内容</option>
<option value="A">A</option>
<option value="b">B</option>
<option value="c">C</option>
</select>
`,//多选 multiple 数据为数组
data() {
return {
message: [],
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<select v-model="message" multiple>
<option value="A">A</option>
<option value="b">B</option>
<option value="c">C</option>
</select>
`,- 使用循环渲染
// 数据为对象数组形式
// 分析: text,value分别是显示数据和返回数据
// 返回数据是我们自己定义也可以是对象的形式 {value: 'A'}
data() {
return {
message: "",
options: [
{ text: "A", value: "A" },
{ text: "B", value: "B" },
{ text: "C", value: "C" },
],
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<select v-model="message">
<option value="" disabled>请输入内容</option>
<option v-for="item in options" :value="item.value"> {{item.text}}
</option>
</select>
`,- 修饰符
//(1).lazy input框中value和数据的及时响应,变成当失焦时才响应
data() {
return {
message: "minyue",
};
},
template: `
{{message}}
<input v-model.lazy="message" />
`,
//(2).number 默认为字符串类型 存入时改变为数字类型
data() {
return {
message: 11,
};
},
template: `
{{typeof message}}
<input v-model.number="message" />
`,
//.trim 去除数据前后的空格
VUE组件
3.1组件的定义,复用性,分类
定义
由根实例拆分出来的一个个小的实例模块
复用性
同一个组件在多次复用时,彼此没有干扰,并且可以在其他子组件中同时复用
分类—全局组件
只要定义了,处处可以使用,性能不高,但是使用起来简单,名字建议 小写字母单词,中间用横线间隔
//利用app.componnet("", {})创建的组件
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>father<hello-world /></div>
<div>father<hello-world /></div>
`,
});
app.component("hello-world", {
template: "<span>son1</span>",
});分类—局部组件
定义了,要注册之后才能使用,性能比较高,使用起来有些麻烦,建议大些字母开头,驼峰命名
const Counter = {
data() {
return {
count: 1,
};
},
template: `<div @click="count += 1">{{count}}</div>`,
};
const HelloWorld = {
template: `<div>hello world</div>`
};
const app = Vue.createApp({
components: {
Counter, HelloWorld,
}, //解构赋值 也可以键值对形式改名
template: `
<counter /> //最好写映射,但Vue也会自动映射 <hello-world />
`,
});3.2组件间传参/参数校验/单向数据流
父组件中以属性形式传递 静态参数或动态参数,子组件同过props 接收,也可以写一些参数进行校验(warning)
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { num: 1234 }
},
template: `
<div><test :content="num" /></div>
`
});
// type:String, Boolean, Array, Object, Function, Symbol
// required 父组件必须传递该参数
// default 默认值 可以直接写值 也可以函数返回
app.component('test', {
props: {
content: {
type: Number,
validator: function(value) {
return value < 1000;
},
default: function() {
return 456;
}
}
},
template: `<div>{{content}}</div>`
});单向数据流
子组件可以使用父组件传递来的参数数据,但绝对不能修改
// 想要修改 就必须自己复刻一个数据再进行修改
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { num: 1 };
},
template: `
<div>
<counter :count="num" />
</div>
`,
});
app.component("counter", {
props: ["count"],
data() {
return {
myCount: this.count,
};
},
template: `<div @click="myCount += 1">{{myCount}}</div>`,
});合并传参
但参数很多时,一个个写很麻烦,使用合并传参
//v-bind="param" 等价于
//:num="params.num" :a="params.a" :b="params.b"
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
param: {
num: 1,
a: 2,
b: 3,
},
};
},
template: `
<div>
<counter v-bind="param" />
</div>
`,
});
app.component("counter", {
props: ["num", "a", "b"],
template: `<div>{{num}}{{a}}{{b}}</div>`,
});3.3 Non-Props属性是什么
前面说到,组件传值,需要子组件中props 接受参数;但是当没有props时,会发生什么?
//Non-props
//(1)最外层只有一个节点时:会像挂载属性一样直接挂载到子组件上
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<counter msg="hello" />
</div>
`
});
app.component('counter', {
//inheritAttrs: false, //表示不接受继承来的属性
template: `
<div>
Counter
</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
//得到 <div msg="hello">Counter</div>//(2)当最外层有多个节点时 Non-props会失效
// 1.使用v-bind="$attrs" 执行全部继承
<div v-bind="$attrs">Counter</div>
// 2.对指定一个属性的继承
<div :msg="$attrs.msg">Counter</div>
<div :msg1="$attrs.msg1">Counter</div>
// 3.子组件其他函数中想要使用到传递来的属性时 this.$attrs访问
mounted() {
console.log(this.$attrs.msg);
},- 多用于style和class的继承
3.4父子组件间通过事件通信
- 子组件发出触发事件,父组件监听事件
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
methods: {
handleAdd(param1,param2) {
this.count += param2;
}
//handleAdd(count) {
// this.count = count;
//}
}
template: `
<counter
:count="count"
@add-one="handleAdd"
/>
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: ['count'],
emits: ['add'],
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('add', 2, 3);
//this.$emit('add', this.count + 4)
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{count}}</div>
`
});子组件—–触发事件—–驼峰式写法
this.$emit('addOne', 2, 3);触发事件梳理—-
emits: []也可以写成对象形式参数校验emits: { addOne: (count) => { if(count >= 0) { return true; } return false; } }父组件—–监听事件—-间隔符写法捕获事件
@add-one="handleAddOne"总结: 父组件传递给子组件一个数据—-子组件请求父组件改变对应数据
- 绑定数据让我们想到双向绑定
v-model
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
template: `
<counter v-model="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: ['modelValue'],
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', this.modelValue + 3);
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});如果想改变名称可以,而且可以多个
v-model的绑定<counter v-model:add="count" />对应改为addupdate 是固定写法 — 底层就是
@change和-bind
- v-model的自定义修饰符
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 'a' }
},
template: `
<counter v-model.uppercase="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: {
'modelValue': String,
'modelModifiers': {
default: ()=>({})
//检测是否有修饰符 如果有就添加到对象中 值为 true
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
let newValue = this.modelValue + 'b';
if(this.modelModifiers.uppercase) {
newValue = newValue.toUpperCase();
}
this.$emit('update:modelValue', this.modelValue + 3);
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});3.5使用插槽 和具名插槽解决组件内容传递
父组件往子组件传递DOM节点时 子组件中用<slot>作为形式DOM,有父组件内部实际DOM
//数据属性,作用域问题--- 父模板里面的数据使用父模板中的数据
//插槽默认值: 父代没有内容时,默认值在子代插槽标签内部
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
//只有layout一层时,不用具名插槽
<layout>
<template v-slot:header> //需要外层结构包裹,双标签!
<div>header</div>
</template>
<template v-slot:footer>
<div>footer</div>
</template>
</layout>
`
});
app.component('layout', {
template: `
<div>
<slot name="header"></slot> //必须配备对应的name
<div>content</div>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</div>
`
});3.6作用域插槽
怎么通过子代插槽标签,传递子代数据到父代对应DOM中使用
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<list v-slot="{item}"> //应该是slotProps 解构!
<div>{{item}}</div>
</list>
`
});
app.component('list', {
data() {return {list: [1, 2, 3]}},
template: `
<div>
<slot v-for="item in list" :item="item" />
//绑定item传递给父代
</div>
`
});3.7动态组件/异步组件
动态组件:根据数据变化,结合<component> ,实现对不同子组件调用的切换
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
currentItem: 'input-item'
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.currentItem =
this.currentItem === 'input-item' ?
'common-item' : 'input-item';
}
},
template: `
<keep-alive>
<compoment :is="currentItem" />
</keep-alive>
<button @click="handleClick">change</button>
`
})
app.component('input-item', {
template: `<input />`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `<div>minyue</div>`
});<keep-alive>可以缓存数据,保存input框输入的数据
异步组件:异步调用渲染的组件形式
const app = Vue.createApp({
template: `
<div>
<common-item /> //同步组件
<async-common-item /> //异步组件
</div>
`
});
app.component('common-item', {
template: `<div>hello world</div>`
});
app.component('async-common-item', Vue.defineAsyncComponent(() => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({
template: `<div>this is an async component</div>`
})
}, 4000)
})
}))Vue.defineAsyncComponent(() => {})返回一个promise 当resolved之后就会触发渲染。
3.8基础语法补充
v-once:表示标签只渲染一次,但绑定事件照样会触发ref: 获取DOM/组件引用,当页面挂载完,可以操作带有ref属性的DOM元素/组件mounted() { console.log(this.$refs.count.innerHTML = 'minyue'); }, template: ` <div ref='count'> {{count}} </div> `,也可以通过这种语法,获取子组件中的函数,并引用
provide/inject跨组件传值const app = Vue.createApp({ data() { return { count: 1 }; }, provide() { //传递变量数据要函数 返回值形式 return { count: this.count, }; }, //provide: { //数据可以直接对象 键值对形式 // count: 1; //} template: ` <div> <child /> <button @click="count += 1">Add</button> </div> `, }); app.component("child", { template: `<child-child />`, }); app.component("child-child", { inject: ["count"], template: `<div>{{count}}</div>`, });当然这种返回都是一次性的 不是双向绑定的关系,数据变化返回值不会更新
vue动画
4.1实现基础的CSS过渡和动画
- CSS帧动画
//style样式
<style>
@keyframes leftToRight {
0% {
transform: translate(-100px);
}
50% {
transform: translate(-50px);
}
0% {
transform: translate(0px);
}
}
.animation {
animation: leftToRight 3s;
}
</style>
//script
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
animate: {
animation: false;
}
}
},
methods() {
handleClick() {
this.animate.animation = !this.animate.animation;
}
},
template: `
<div :class="animate">hello world</div>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
`
});- 过渡
//style 样式
.transition {
transition: 3s background-color ease;
}
.blue {
background: blue;
}
.green {
background: green;
}
//script
data() {
return {
animate: {
transition: true,
blue: true,
green: false,
}
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.animate.blue = !this.animate.blue;
this.animate.green = !this.animate.green;
}
},
template: `
<div>
<div :class="animate">hello world</div>
<button @click="handleClick">切换</button>
</div>
`- 同样也可以通过样式对象来,使用行内样式来实现。
4.2<transition>标签实现单元素组件过渡和动画
- 过渡写法
//过渡css transition标签对应固定写法
.v-enter-from {
opacity: 0; //入场效果的初态
}
.v-enter-active {
transition: opacity 3s ease-out; //如何执行动画
}
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1; //入场效果的终态
}
.v-leave-from {
opacity: 1; //可以省略
}
.v-leave-active {
transition: opacity 3s ease-in;
}
.v-leave-to {
opacity: 0;
}//transition标签包裹需要动画效果的标签
//当按钮改变show的值,标签展示隐藏时,就会触发动画
<transition>
<div v-if="show">hello</div>
</transition> - 动画写法
//(1)关键帧
@keyframes shake {
0% {
transform: translateX(-100px)
}
50% {
transform: translateX(-50px)
}
100% {
transform: translateX(50px)
}
}
.v-enter-active {
animation: shake 3s;
}
.v-leave-active {
animation: shake 3s;
}<transform>标签添加name属性,, 使用对应name-代替默认的v-也可以直接自定义class的名字
<transition enter-active-class="hello" leave-active-class="bye" > //..... </transition>自定义动画方便和第三方库结合
https://animate.style/<transition enter-active-class="animate__animated animate__bounce" leave-active-class="animate__animated animate__bounce" > //..... </transition>显然动画和过渡可以同时添加在transition标签中。思考,时间不同一,怎么办?
transition标签上添加属性type="transition"表示以过渡为准- 绑定属性
:duration="1000"强制1秒完成 ,:duration={enter:1000,leave:2000}表示入场动画1秒,出场动画2秒
- 使用js实现动画效果
//(1)css禁用 调用transition过程的钩子函数
methods: {
handleBeforeEnter(el) {
el.style.color = "red";
},
handleEnterActive(el,done) {
const animation = setInteval(() => {
const color = el.style.color;
if (color === "red") {
el.style.color = 'green';
} else {
el.style.color = 'red';
}
}, 1000);
setTimeOut(() => {
clearInterval(animation);
done();
}, 3000)
},
handleEnterEnd((el)=>{
alert(123); //当Active函数中调用了 done()后才能执行
})
}
<transiton
:css="false" //禁用css
@before-enter="handleBeforeEnter" //el
@enter="handleEnterActive" //el done
@after-enter="handleEnterEnd" //el
>
//....
</transition>4.3组件和元素切换动画实现
- 多个单元素标签之间的切换
<transition mode="out-in" appear> //动画先出后进,首次入场动画
<div v-if="show">hello</div> //show变量值控制两个标签的切换
<div v-else="show">bye</div>
</transition>mode="out-in": 动画先出后进,避免出现和消失同时呈现appear: 首次展示的DOM也会有动画
- 多个组件之间切换
//除了使用 组件 if-show以外,还可以使用component动态组件
data() {
return {
component: 'component-a'
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.component = this.component==='component-a'
?'component-b':'component-a';
}
},
//
<transition mode="out-in" appear>
<component :is="component" />
</transition>4.4列表添加删除动画
//style v-move 其他项移动会有的动画
.v-enter-from {
opacity: 0;
transform: translateY(30px);
}
.v-enter-active {
transition: all .5s ease-in;
}
.v-enter-to {
opacity: 1;
transform: translateY(0);
}
.v-move {
transition: all .5s ease-in;
}
.list-item {
display: inline-block; //同行显示
margin-right: 10px;
}
//vue 使用到 transition-group
data() {
return { list: [1, 2, 3] }
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.list.unshift(this.list.length + 1);
},
},
template: `
<div>
<transition-group>
<span class="list-item" v-for="item in list" :key="item">{{item}}</span>
</transition-group>
<button @click="handleClick">增加</button>
</div>
`4.5状态动画
数据的变化—>所看到的动画
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
number: 1,
animateNumber: 1
}
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.number = 10;
if(this.animateNumber < this.number) {
const animation = setInterval(() => {
this.animateNumber += 1;
if(this.animateNumber === 10) {
clearInterval(animation);
}
}, 100);
}
},
},
template: `
<div>
<div>{{animateNumber}}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">增加</button>
</div>
`
});vue高级用法
5.1mixin混入
- 组件 :data, methods 优先级高于 mixin data, methods 优先级
- 生命周期函数:先执行 mixin 里面的,再执行组件里面的
- 自定义的属性,组件种的属性优先级高于 mixin 属性的优先级
//局部mixin添加一句 mixins: [myMixin]
//全局mixin app.mixin({})//自定义属性 this.$options.number
const myMixin = {
number: 1
}
const app = Vue.createApp({
mixins: [myMixin],
number: 2,
template: `
<div>
<div>{{this.$options.number}}</div>
</div>
`
});
//自定义优先级
app.config.optionMergeStrategies.number = (mixinVal, appValue) => {
return mixinVal || appValue;
}5.2自定义指令
比如:自动聚焦实现
//(1)可以使用生命周期函数实现
mounted() {
this.$refs.input.focus();
},
template: `
<input ref="input" />
`//(2)创建自定义指令 directive
<input v-focus /> //可以实现同样效果
//全局的自定义指令
app.directive('focus', {
mounted(el) {
el.focus();
},
})
//局部自定义指令
const directive = {
focus: {
mounted(el) {
el.focus();
},
},
}